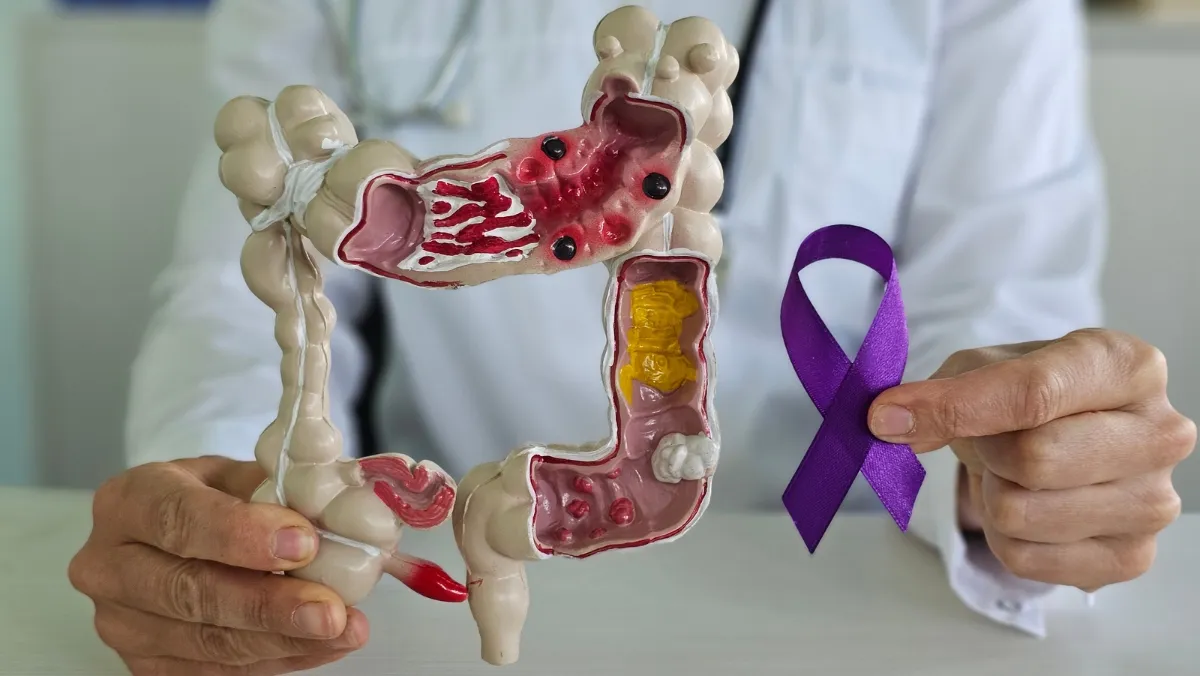
Bowel cancer screening is a preventive health measure aimed at detecting early signs of colorectal cancer before symptoms appear. By identifying abnormalities at an early stage, screening significantly improves treatment outcomes and survival rates. In urban centers like Chennai, increased awareness and access to medical diagnostics have led to a growing emphasis on regular checkups. Opting for a bowel cancer screening test in Chennai ensures timely intervention through advanced healthcare infrastructure. Early detection not only saves lives but also reduces the long-term burden on patients and healthcare systems.
Bowel cancer risk increases due to a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and medical factors. Identifying these risks early supports timely decisions about undergoing a bowel cancer screening test in Chennai or nearby areas like Tharamani and Kottivakkam.
Bowel cancer symptoms may be mild at first but should not be overlooked. Early detection through a bowel cancer screening test in Chennai, Tharamani, or Kottivakkam is crucial when any of the following signs appear.
Timely screening is essential for detecting bowel cancer in its early stages. Individuals are encouraged to undergo a bowel cancer screening test in Chennai, Tharamani, or Kottivakkam based on risk factors and symptoms.
The treatment approach for bowel cancer depends on the stage of the disease, overall health, and tumor location. Early diagnosis through a bowel cancer screening test in Chennai, Tharamani, or Kottivakkam often leads to more effective and less invasive treatment options.
Bowel cancer prevention relies on healthy lifestyle choices and regular, timely screenings. Accessing a bowel cancer screening test in Chennai, Tharamani, or Kottivakkam can significantly reduce the risk through early detection.
Bowel cancer remains one of the most preventable and treatable forms of cancer when detected early through timely screening. With access to advanced medical facilities, the bowel cancer screening test in Chennai offers individuals a vital opportunity to identify risks before symptoms progress. Early diagnosis through reliable methods such as colonoscopy or FOBT can significantly reduce the need for aggressive treatment and improve long-term outcomes.
Prioritizing routine screening and maintaining awareness of personal risk factors are essential steps toward prevention. Individuals, especially those above 50 or with a family history, are encouraged to take an active role in their health through regular screening.
Read also: Irritable Bowel
A blood test alone cannot diagnose bowel cancer, but it can help detect markers that indicate potential issues. Doctors often use blood tests alongside other diagnostic methods, such as stool tests, colonoscopy, or imaging scans, to confirm the presence of bowel cancer and monitor overall health during diagnosis and treatment planning.
Reducing the risk of bowel cancer involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle and regular screenings. Eat a diet rich in fiber, fruits, and vegetables, limit red and processed meats, avoid smoking and excessive alcohol, exercise regularly, and maintain a healthy weight. Regular screening tests help detect polyps early, preventing them from developing into cancer.
Bowel cancer pain is often felt in the abdominal area, typically as cramps or discomfort that may come and go. The pain might localize in the lower abdomen but can also radiate depending on the tumor’s location. Persistent abdominal pain, especially when combined with changes in bowel habits, should be evaluated by a doctor.